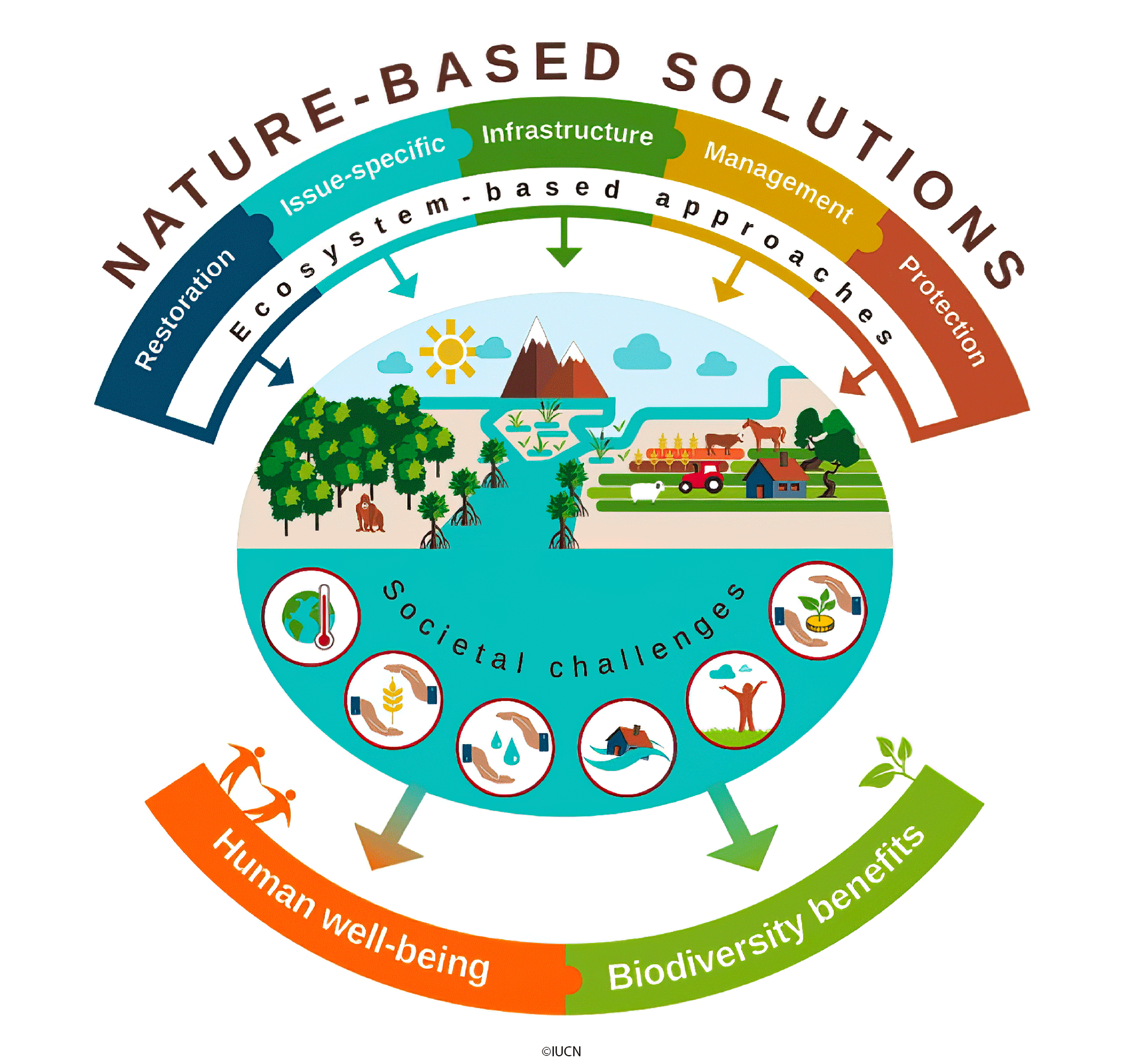
Nature-Based Solutions
Nature Based Solutions (NBS) have emerged as a promising way to address societal challenges like climate change, water scarcity, and natural disasters. By leveraging the power of nature and its ecosystems, NBS offers cost-effective, sustainable solutions that provide multiple benefits for both humans and the environment. This growing area of research and activity includes a range of solutions, such as restoring degraded ecosystems, preserving natural habitats, and integrating green infrastructure into urban areas. As awareness of the impacts of human activities on the planet continues to grow, NBS is increasingly being recognized as an essential component of building more resilient societies. By harnessing the natural resources around us, we can find innovative solutions to some of the most pressing environmental challenges of our time.